What Is The Meaning Of Intracerebral Hematoma
Bleeding in the brain is classified into intra axial and extra axial subtypes ich its an intra-axial hemorrhage characterized by blood in the brain pa. Most ICHs are related to cerebral contusions.
 Definition Of Intracerebral Hematoma
Definition Of Intracerebral Hematoma
What is the definition or description of.

What is the meaning of intracerebral hematoma. An intracerebral hematoma is an uncommon yet life-threatening condition in which one or more blood vessels rupture in the brain. Intracerebral hemorrhage ICH is when blood suddenly bursts into brain tissue causing damage to your brain. An intracerebral hemorrhage ICH is usually caused by rupture of tiny arteries within the brain tissue left.
The name means within the cerebrum or brain. An intracerebral hematoma ICH is a well-defined collection of blood within the brain parenchyma functional tissue. Intracerebral hemorrhage also known as cerebral bleed and intraparenchymal bleed is a sudden bleeding into the tissues of the brain into its ventricles or into both.
This bleeding occurs in the lobes pons and cerebellum of the brain bleeding anywhere within the brain tissue itself including the brainstem. Bleeding within the brain. Send thanks to the doctor.
They include headache weakness. An ICH can occur close to the surface or in deep areas of the brain. Intracerebral hematoma synonyms Intracerebral hematoma pronunciation Intracerebral hematoma translation English dictionary definition of Intracerebral hematoma.
The bleeding can be minor such as when the superficial vessels in the skin are damaged leading to petechiae and ecchymosis. Treatment is by surgery. As blood collects a hematoma or blood clot forms causing increased pressure on the brain.
Hemorrhage is an acute loss of blood from a damaged blood vessel. The bleeding can be minor such as when the superficial vessels in the skin are damaged leading to petechiae and ecchymosis. ICHs complicate head injury in 2 to 3 of all head-injured patients.
Diagnosis is usually by MRI or CAT scan. Hematomas or hematomata A localized swelling filled with blood resulting from a break in a blood vessel. A hematoma is most likely to occur after a severe head injury though drug overdoses chronic hypertension and blood disorders can also cause sudden bleeding.
There are many causes including trauma rupture of a bulging blood vessel aneurysm poorly connected arteries and veins from birth high blood pressure and tumors. Intracerebral hemorrhage is when theres bleeding inside of your brain. Often symptoms get worse over time.
Intracerebral Hemorrhage When blood vessels within the brain become damaged they are more likely to burst and cause a hemorrhage. Intracranial hemorrhage thalamic hemorrhage Neurology Hemorrhage in the brain often cause by hypertensive small vessel disease Locations Lobar or deepaffecting the thalamus basal ganglia pons cerebellum Etiology Trauma vascular defectsaneurysm hemangioma HTN idiopathic Pathophysiology Cerebral edema and hematoma result in intracranial pressure with destruction of brain tissue Clinical Sx are usually abrupt and occur without warning often during activity less commonly. Causes include brain trauma aneurysms arteriovenous malformations and bra.
Two types of brain bleeds can occur inside the brain tissue itself intracerebral hemorrhage also called cerebral hemorrhage and hemorrhagic stroke and intraventicular hemorrhage. Bleeding in the brain is classified into intra axial and extra axial subtypes ich its an intra-axial hemorrhage characterized by blood in the brain parenchyma brain tissue bruise ich can be caused by accelerating-decelerating trauma or spontaneous hemorrhage spontanouse hemorrhage can be caused by hemorrhagic stroke rupture of an aneurysm avm and others risk factors are hypertension diab. Fever is also common.
Intracerebral hemorrhage occurs when a diseased blood vessel within the brain bursts allowing blood to leak inside the brain. It is one kind of bleeding within the skull and is one kind of stroke. Septal hematomas occur in the area behind the nose called the septum.
Subcutaneous hematomas occur beneath the skin when blood accumulates in fat rather than muscle following impact or injury. They involve blood pooling either inside your brain intracerebral hematoma or between your skull and brain epidural hematoma. Hematomas or hematomata A localized swelling filled with blood resulting from a break in a blood vessel.
Symptoms usually appear suddenly during ICH. Symptoms can include headache one-sided weakness vomiting seizures decreased level of consciousness and neck stiffness. Intracerebral intraparenchymal hematoma This type of hematoma also known as intraparenchymal hematoma occurs when blood pools in the tissues of the brain.
Hemorrhage. This is the most common type of ICH that occurs with a stroke. Bleeding in the brai.
Intracerebral hematoma synonyms Intracerebral hematoma pronunciation Intracerebral hematoma translation English dictionary definition of Intracerebral hematoma. Its not usually the result of injury. -mas -mata a circumscribed.
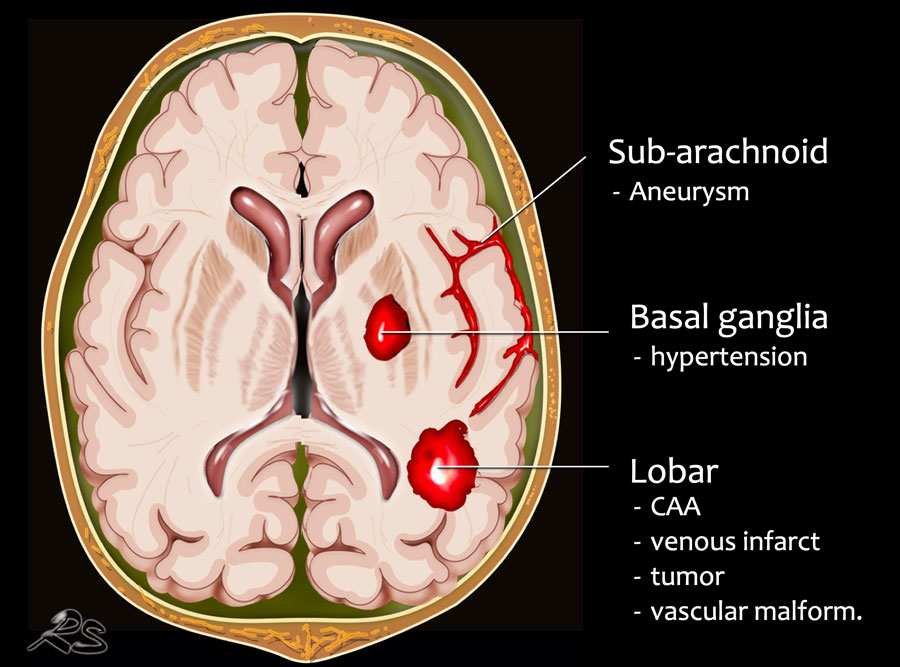 The Radiology Assistant Non Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage
The Radiology Assistant Non Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage
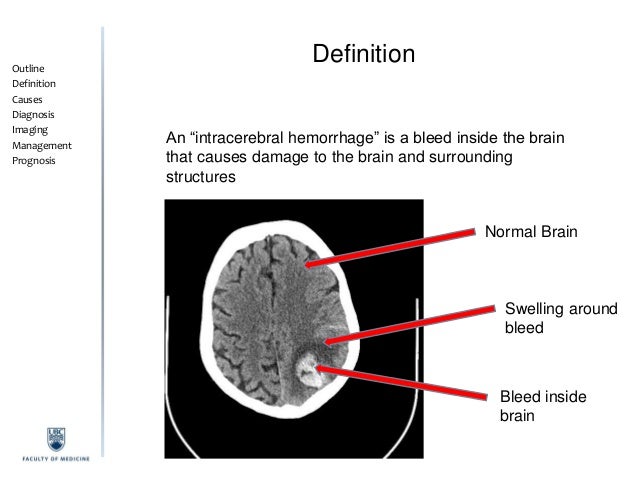 Intracerebral Hemorrhage Info For Patients And Families
Intracerebral Hemorrhage Info For Patients And Families
 Intracerebral Hemorrhage Symptoms Risk Factors And Treatment
Intracerebral Hemorrhage Symptoms Risk Factors And Treatment
 Intracerebral Hemorrhage Neurologic Disorders Merck Manuals Professional Edition
Intracerebral Hemorrhage Neurologic Disorders Merck Manuals Professional Edition
 Intracerebral Hemorrhage Neurologic Disorders Merck Manuals Professional Edition
Intracerebral Hemorrhage Neurologic Disorders Merck Manuals Professional Edition
 Intracerebral Hemorrhage Wikiwand
Intracerebral Hemorrhage Wikiwand
 Intracerebral Haemorrhage Current Approaches To Acute Management The Lancet
Intracerebral Haemorrhage Current Approaches To Acute Management The Lancet
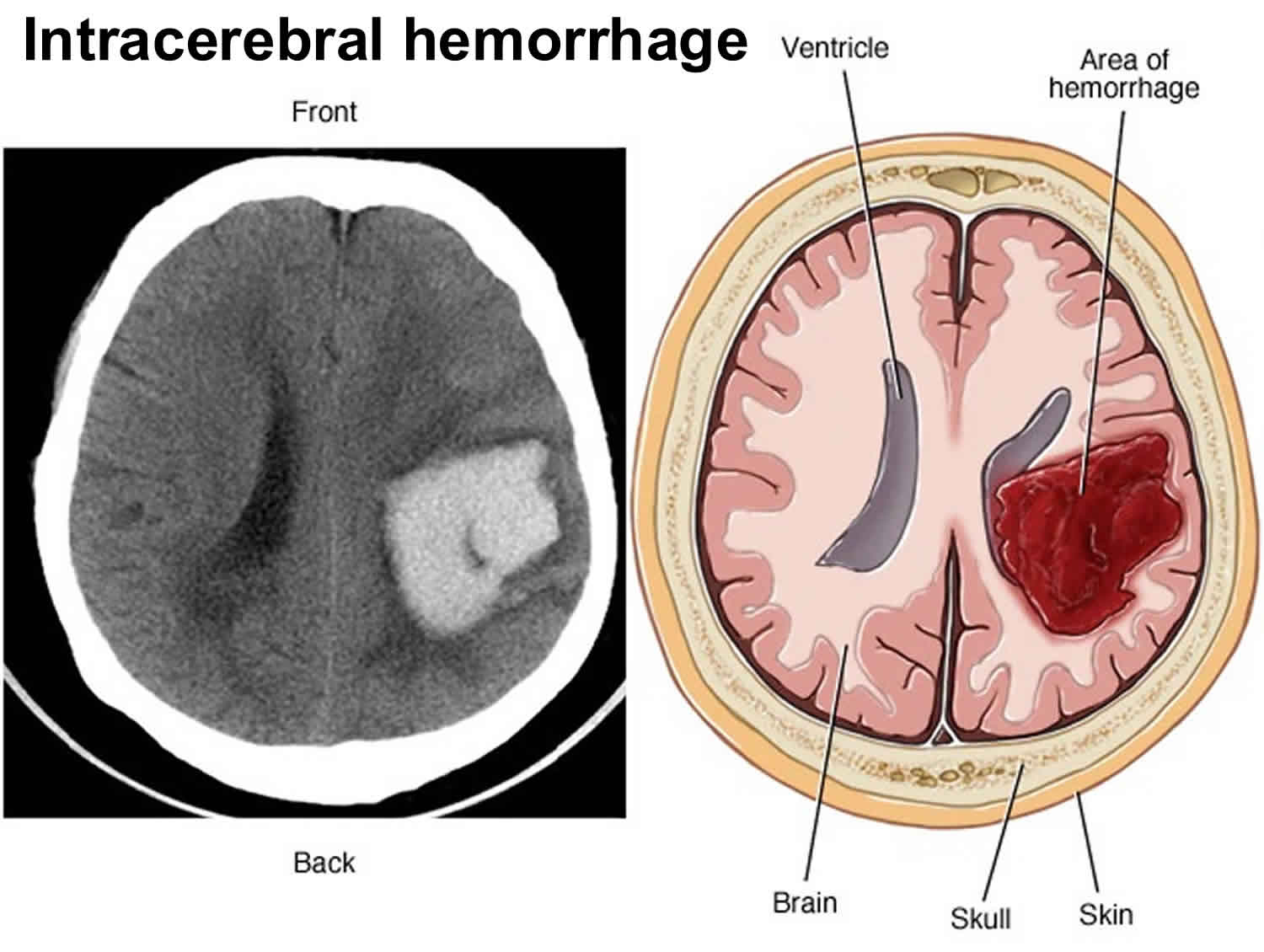 Intracerebral Hemorrhage Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Recovery
Intracerebral Hemorrhage Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Recovery
 Infant Intracranial Hemorrhages Brain Bleeds Causes Signs Symptoms
Infant Intracranial Hemorrhages Brain Bleeds Causes Signs Symptoms
 Repeat Ct Scan Of The Brain A A Large Intracerebral Hemorrhage In Download Scientific Diagram
Repeat Ct Scan Of The Brain A A Large Intracerebral Hemorrhage In Download Scientific Diagram
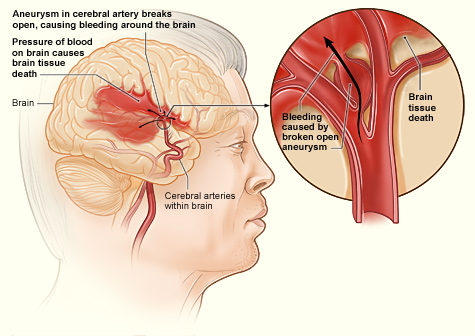 Hemorrhagic Stroke Intracerebral Hemorrhage Physiopedia
Hemorrhagic Stroke Intracerebral Hemorrhage Physiopedia
 Intracerebral Hemorrhage Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Intracerebral Hemorrhage Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
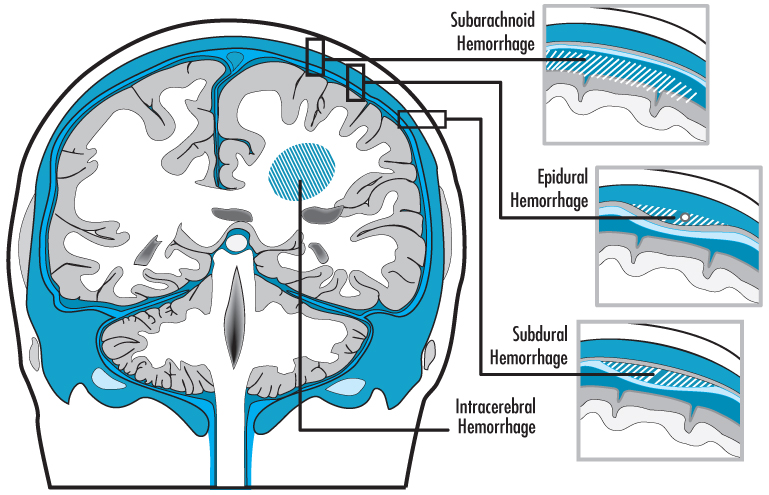 Traumatic Brain Injuries And Hematomas
Traumatic Brain Injuries And Hematomas
 Intracerebral Hemorrhage Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Intracerebral Hemorrhage Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
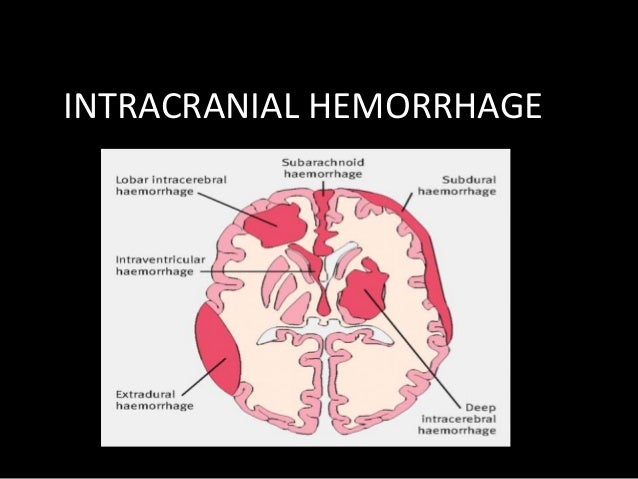 Intracranial Hemorrhage Shruthi S Jayaraj Calicut Medical College
Intracranial Hemorrhage Shruthi S Jayaraj Calicut Medical College
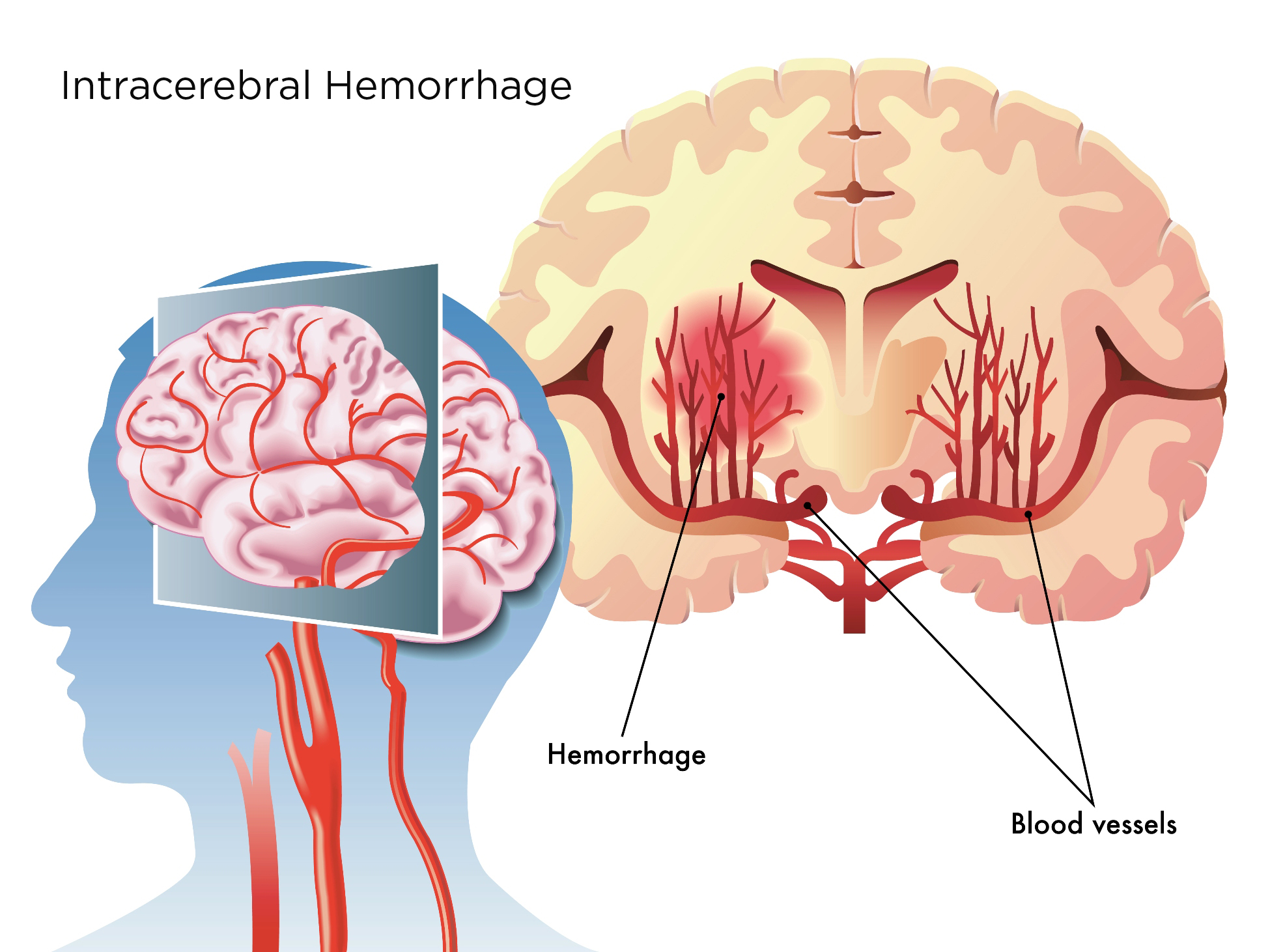 Intracerebral Hemorrhage Symptoms Treatment Pacific Stroke Neurovascular Center
Intracerebral Hemorrhage Symptoms Treatment Pacific Stroke Neurovascular Center

