Workup For Gross Hematuria
The color change does not necessarily reflect the degree of blood loss since as little as 1 mL of blood per liter of urine can induce a visible color change. When visible to the patient it is termed gross hematuria while microscopic hematuria is not visible to the naked eye but rather detected by the microscopic examination of the urinary sediment.
 National Practice Recommendations For Hematuria How To Evaluate In The Absence Of Strong Evidence Abstract Europe Pmc
National Practice Recommendations For Hematuria How To Evaluate In The Absence Of Strong Evidence Abstract Europe Pmc
COMMON POTENTIALLY SERIOUS Hematuria is common.

Workup for gross hematuria. Gross hematuria indicates that there are enough blood cells present to change the color of the urine. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM R310 became effective on October 1 2020. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of R310 - other international versions of ICD-10 R310 may differ.
It can detect trace amounts of. A urologist also should evaluate children with recurrent nonglomerular macroscopic hematuria of undetermined origin because cystoscopy may be warranted. Description gross hematuria is visible blood in urine usually pink or red in color that may be a symptom of either benign and malignant conditions 1 2 5 in adults who undergo a full workup the cause of gross hematuria is identified in about 90 of cases Nat Rev Urol 2010 Apr7 4189.
The most important test in the evaluation of hematuria is a microscopic examination of the urine. Rithmic approach to the workup FIGURE 1 and reviews the further evaluation of patients with hematuria. Kidney stones Smaller stones sometimes can be flushed from the urinary tract by drinking lots of fluids.
The visible presence of blood in the urine can range in color from bright red to dark brown. Hematuria - American Urological Association Hematuria is defined as the presence of red blood cells in the urine. Evaluation and workup indicates that there is a tumor a structural urogenital abnormality or an obstructing calculus.
This work sought to mitigate potentially avoidable risks and costs associated with the over-evaluation of patients at low risk for malignancy while at the same time addressing the delays in diagnosis of important urologic conditions caused by widespread under-evaluation and variations in care. In some cases no treatment is necessary. Microscopic hematuria Microscopic hematuria defined by more than.
3 Hematuria can be due to an isolated. 6 Approximately 10 mL of midstream urine should be collected and immediately centrifuged at 2000. Asymptomatic Gross Hematuria Exercise-induced hematuria transient usually resolves within 48 hours Hematologic hemophilia thrombocytopenia coagulopathy malignancy Recurrent episodes of gross hematuria often in presence of bodily stressor such as illness IgA nephropathy Alport syndrome Thin basement membrane disease.
Larger stones may require surgery or lithotripsy a procedure that breaks up the stone. When to see a doctor. The AUA panel aimed to develop and disseminate clear guideline recommendations for the evaluation of hematuria.
It takes little blood to produce red urine and the bleeding usually isnt painful. For example in one study225 of men ages 28 to 57 tested positive for heme when screened by dipstick testing as did 54 of men ages 18 to 54 in another study. Bloody urine often occurs without other signs or symptoms.
The urine dipstick test is currently one of the most useful and sensitive tools in detecting hematuria. Antibiotics typically will cure infection-related hematuria. 24 hour Urine Collection 24 Hour Urine Protein Clean Catch Urine Collection Epitestosterone to Testosterone Ratio Expressed Prostatic Secretion Free PSA Free Testosterone Gross Hematuria Microscopic Hematuria Prostate Specific Antigen Semen Analysis Split 24 Hour Urine Protein Sulfosalicylic Acid Test Total Testosterone Urinalysis Urinary Cast Urine Appearance Urine Bilirubin Urine Crystal Urine Culture Urine Glucose Urine Hemoglobin Urine Hemosiderin Urine Ketone Urine Leukocyte Esterase.
Gross hematuria produces pink red or cola-colored urine due to the presence of red blood cells. This test is based on the peroxidase activity of hemoglobin. Passing blood clots in your urine however can be painful.
For other causes of hematuria treatment may be more complex. R310 is a billablespecific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Hematuria may be visible to the naked eye called gross hematuria or detectable only on examination of the urine sediment by microscopy called microscopic hematuria.
Treatment Depending on the condition causing your hematuria treatment might involve taking antibiotics to clear a urinary tract infection trying a prescription medication to shrink an enlarged prostate or having shock wave therapy to break up bladder or kidney stones. Gross hematuria Gross hematuria is suspected because of the presence of red or brown urine. Recommended investigations for haematuria include computed tomography intravenous pyelogram urine cytology urine microscopy and culture and blood tests full blood examination renal function and in men prostate-specific antigen.
Gross hematuria clearly conveys a much higher risk of malignancy than microscopic disease and should be thoroughly evaluated 4 5 but virtually all cases of hematuria as defined by AUA guidelines.
 Assessment Of Asymptomatic Microscopic Hematuria In Adults American Family Physician
Assessment Of Asymptomatic Microscopic Hematuria In Adults American Family Physician
 Adult Hematuria Workup Algorithm C S Culture And Sensitivity Download Scientific Diagram
Adult Hematuria Workup Algorithm C S Culture And Sensitivity Download Scientific Diagram
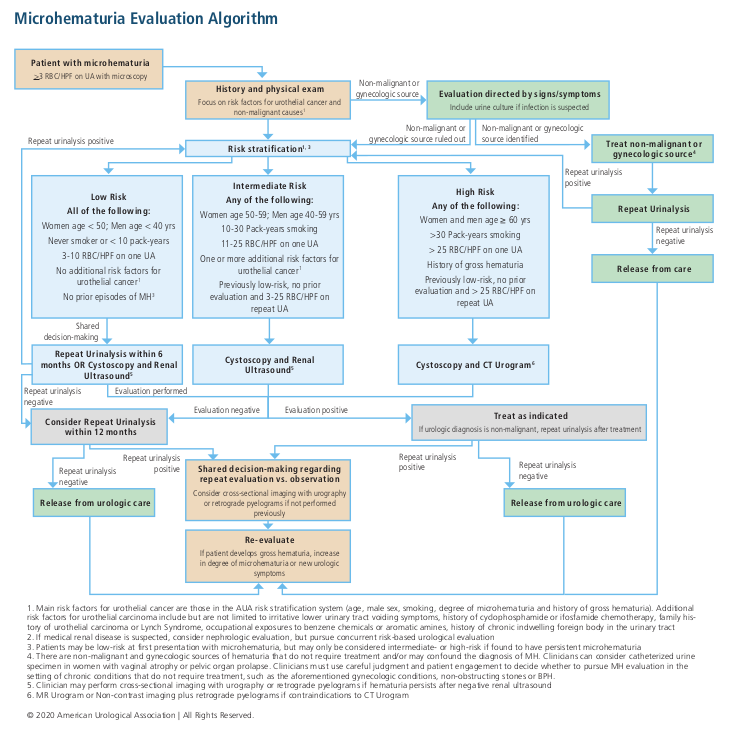 New 2020 Aua Hematuria Guidelines Department Of Urology
New 2020 Aua Hematuria Guidelines Department Of Urology
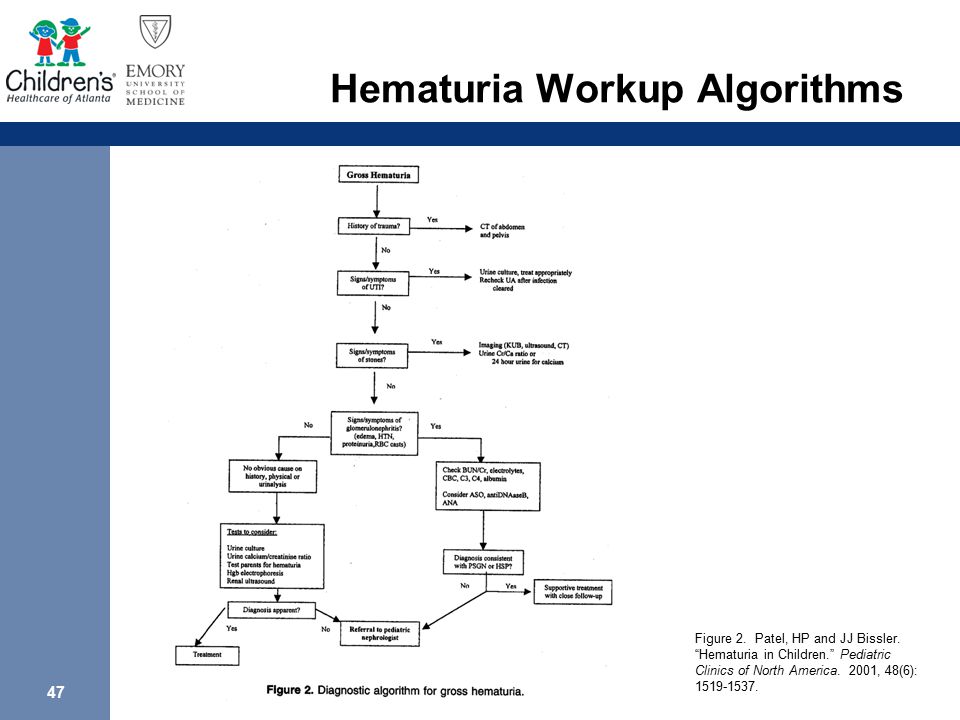 When It Looks Like Kool Aid A Brief Look At Hematuria Ppt Download
When It Looks Like Kool Aid A Brief Look At Hematuria Ppt Download
 The Need For Repeated Urological Evaluation In Low Risk Patients With Microscopic Hematuria After Negative Diagnostic Work Up Anticancer Research
The Need For Repeated Urological Evaluation In Low Risk Patients With Microscopic Hematuria After Negative Diagnostic Work Up Anticancer Research
 Racgp Macroscopic Haematuria A Urological Approach
Racgp Macroscopic Haematuria A Urological Approach
 Figure 1 From Assessment Of Asymptomatic Microscopic Hematuria In Adults Semantic Scholar
Figure 1 From Assessment Of Asymptomatic Microscopic Hematuria In Adults Semantic Scholar
 Asymptomatic Microscopic Hematuria In Adults Summary Of The Aua Best Practice Policy Recommendations American Family Physician
Asymptomatic Microscopic Hematuria In Adults Summary Of The Aua Best Practice Policy Recommendations American Family Physician
 Assessment Of Asymptomatic Microscopic Hematuria In Adults American Family Physician
Assessment Of Asymptomatic Microscopic Hematuria In Adults American Family Physician
 Bladder Cancer Diagnosis And Treatment American Family Physician
Bladder Cancer Diagnosis And Treatment American Family Physician
 Diagnostic Tree For Initial Management Of Asymptomatic Hematuria And Download Scientific Diagram
Diagnostic Tree For Initial Management Of Asymptomatic Hematuria And Download Scientific Diagram
 Evaluation Of Asymptomatic Microscopic Hematuria In Adults American Family Physician
Evaluation Of Asymptomatic Microscopic Hematuria In Adults American Family Physician
 Assessment Of Asymptomatic Microscopic Hematuria In Adults American Family Physician
Assessment Of Asymptomatic Microscopic Hematuria In Adults American Family Physician
 Assessment Of Asymptomatic Microscopic Hematuria In Adults American Family Physician
Assessment Of Asymptomatic Microscopic Hematuria In Adults American Family Physician
 Aua Guideline Addresses Diagnosis Evaluation And Follow Up Of Asymptomatic Microhematuria Practice Guidelines American Family Physician
Aua Guideline Addresses Diagnosis Evaluation And Follow Up Of Asymptomatic Microhematuria Practice Guidelines American Family Physician
 Evaluation And Workup Of Hematuria In Adults Physician Assistant Clinics
Evaluation And Workup Of Hematuria In Adults Physician Assistant Clinics
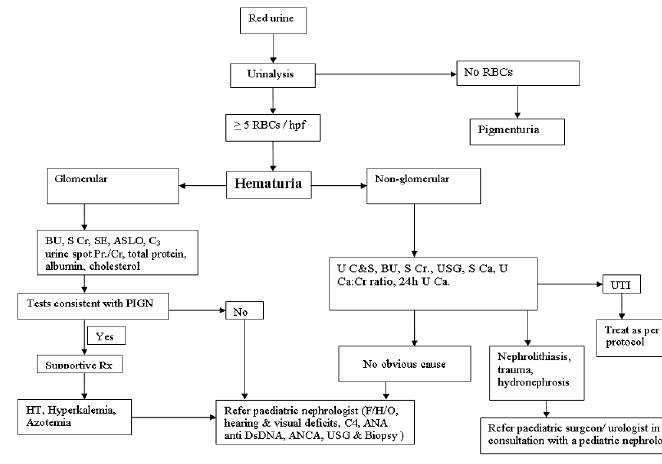
 Flowchart For Clinical Evaluation Of Gross Hematuria For Pediatric Download Scientific Diagram
Flowchart For Clinical Evaluation Of Gross Hematuria For Pediatric Download Scientific Diagram